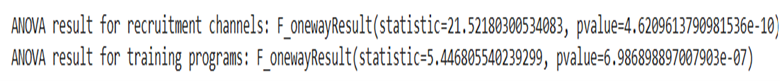Predicting & Enhancing Employee Performance Through HR Analytics
In this project, we utilized HR analytics to predict and enhance employee performance, leveraging a comprehensive dataset and various machine learning models.
In today’s competitive business landscape, organizations strive to enhance productivity and retain top talent. Employee performance is a critical factor influencing organizational success, and optimizing this performance is a primary objective for Human Resources (HR) departments. Leveraging data analytics within HR, commonly referred to as HR analytics, provides a powerful means to achieve this objective. By systematically analyzing employee data, organizations can uncover insights into key performance drivers, optimize recruitment strategies, and evaluate the effectiveness of training programs.
Project Overview:
- Objective: Optimize employee performance using HR data analytics.
Dataset: Employee’s Performance for HR Analytics, souced by Kaggle.
Dataset Features:
- Employee ID: Unique identifier for tracking performance.
- Department: The department in which the employee works.
- Region: Geographical location of the employee.
- Education: Employee’s educational background.
- Gender: Gender of the employee.
- Recruitment Channel: Source of recruitment.
- Number of Trainings: Number of training programs attended.
- Age: Age of the employee.
- Previous Year Rating: The performance rating of the prior year.
- Length of Service: Number of years the employee has worked in the company.
- KPIs Met More Than 80: Number of key performance indicators met.
- Awards Won: Number of awards won.
- Average Training Score: Average score from training programs.
Business Problem/Hypothesis:
- Identify key predictors of employee performance.
- Assess the impact of recruitment channels and training programs on performance.
- Hypothesize that KPIs met, previous ratings and training scores are significant predictors.
Methods/Analysis
- Data Preparation: Handled missing values, performed summary statistics, and data cleaning.
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): Visualized data distributions, outliers, and relationships.
- Statistical Tests: Conducted ANOVA tests to assess recruitment and training impact.
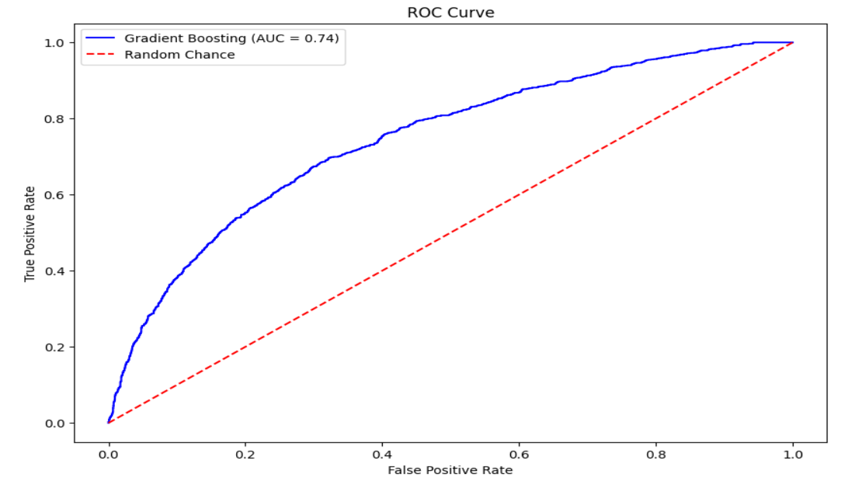
- ROC Curve:
- The ROC curve is above the diagonal, indicating that the model performs better than random guessing.
- The AUC value of 0.74 suggests that the Gradient Boosting model has decenter performance in predicting the target variable.
- Feature Engineering: Transformed categorical variables for modeling.
- Modeling: Used Logistic Regression, Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, and SVM. Tuned Gradient Boosting for optimal performance.
Results
- Model Performance: Gradient Boosting achieved the highest accuracy (0.718).
| Model | Accuracy | Precision (Class 0) | Precision (Class 1) | Recall (Class 0) | Recall (Class 1) | F1 Score (Class 0) | F1 Score (Class 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 0.715 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.87 | 0.43 | 0.80 | 0.52 |
| Random Forest | 0.707 | 0.73 | 0.63 | 0.86 | 0.42 | 0.79 | 0.50 |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.718 | 0.73 | 0.66 | 0.89 | 0.41 | 0.80 | 0.50 |
| SVM | 0.708 | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.91 | 0.34 | 0.80 | 0.45 |
Class 0 - Not Met KPIs / Class 1 - Met KPIs
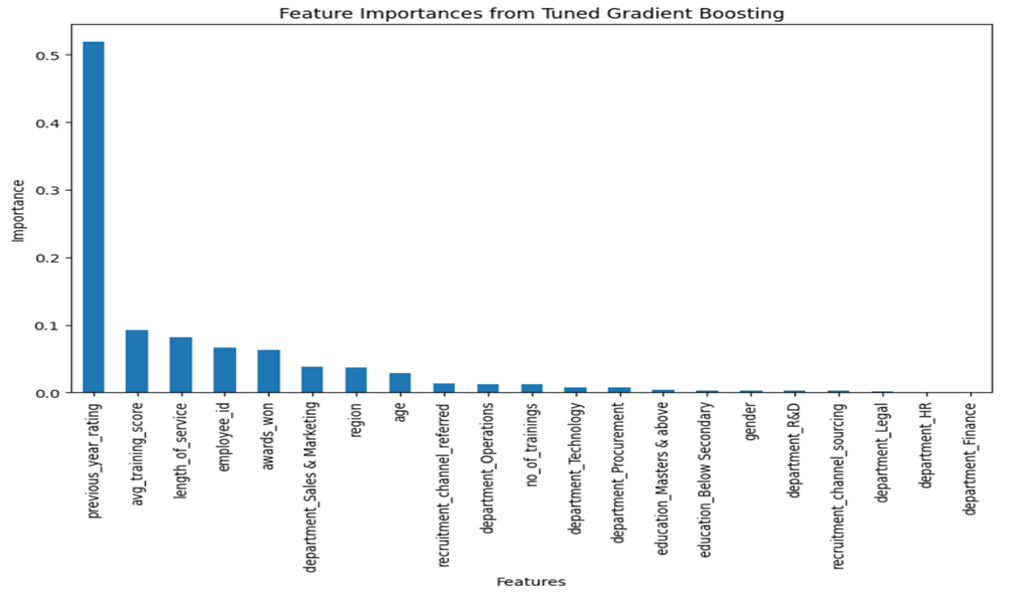
Feature Importance: Identified previous year ratings, training scores, and length of service as top predictors.
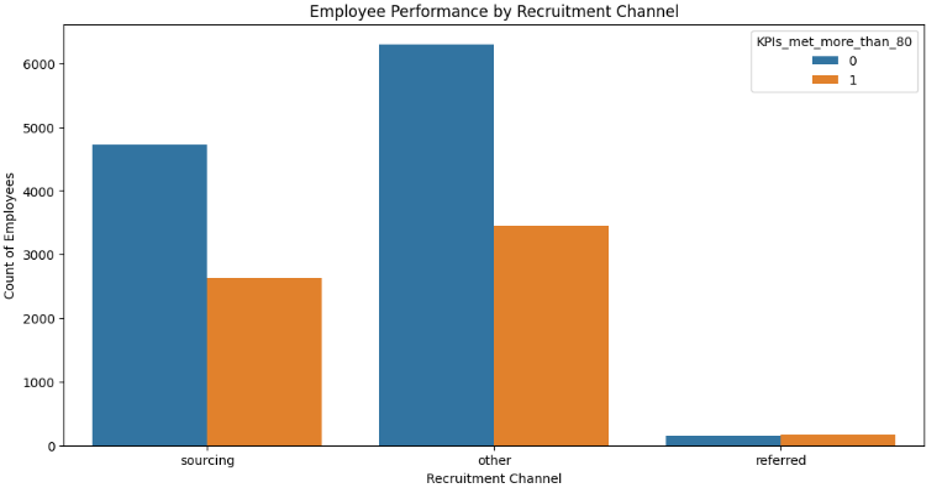
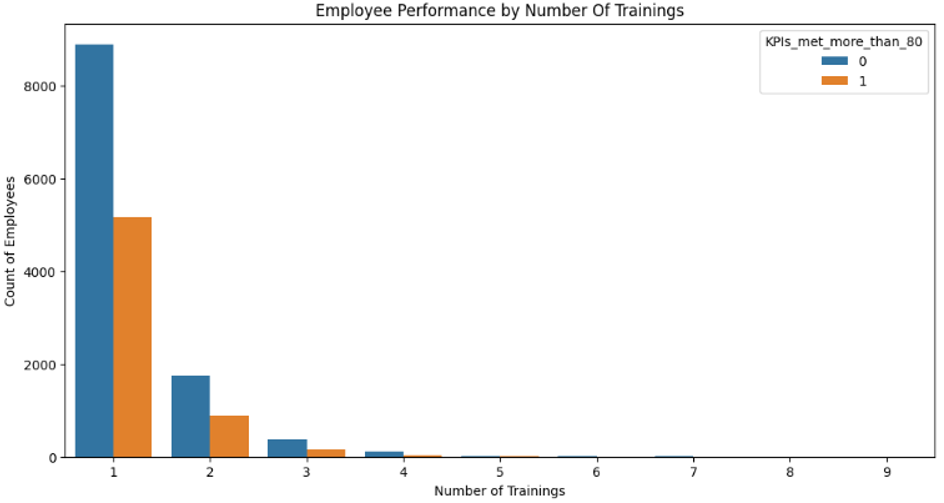
Impact Analysis: Analyzed performance distribution across recruitment channels and training programs.
Recommendations
- Enhance training quality and relevance.
- Optimize recruitment strategies.
- Leverage key performance predictors for HR decisions.
- Implement regular performance monitoring and feedback mechanisms.
Conclusion
This study utilized HR analytics to predict and enhance employee performance, identifying key performance drivers and evaluating HR strategies. The top predictors of performance were previous year ratings, average training scores, and length of service. Recruitment channels and the quality of training programs also significantly impacted performance.
Practical Applications:
- Optimizing Recruitment:
- Strengthen high-performing channels like ‘Other’ and ‘Referred.’
- Improve sourcing strategies with rigorous screening and aligned job descriptions.
- Enhancing Training Programs:
- Focus on quality and relevance.
- Develop tailored and interactive training.
- Offer continuous learning opportunities.
- Leveraging Key Predictors:
- Improve performance reviews.
- Create targeted development programs for training scores and service length.
- Performance Monitoring:
- Implement regular check-ins, 360-degree feedback, and performance dashboards.
- Predictive Model Implementation:
- Use the Gradient Boosting model to predict performance.
- Integrate it into HR systems for real-time insights.
- Update it with new data regularly.
Implementing these strategies can enhance performance, productivity, and work environment. This study highlights the value of HR analytics for strategic decisions and underscores the importance of data-driven HR strategies for organizational success. Future research should address limitations and explore additional features to improve predictive accuracy.